
Virtual remote appointments are available. Contact us for a video telehealth evaluation.

All appointments conducted by our Board Certified doctor and not assistants or non-physician providers.
Frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis, is a painful condition characterized by the gradual loss of shoulder movement. Traditional treatments include physical therapy, medications, and in severe cases, surgery. However, a newer and less invasive approach, frozen shoulder embolization, is saving patients from invasive surgery.
Understanding Frozen Shoulder
Frozen shoulder involves the inflammation and thickening of the shoulder joint capsule, limiting its range of motion. While the exact cause is often unclear, certain risk factors have been identified, including age, gender, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes. The condition progresses through painful stages, impacting daily activities and significantly reducing the affected individual’s quality of life.1
Conventional Frozen Shoulder Treatments
Physical Therapy and Medications
Common approaches to manage frozen shoulder include physical therapy and anti-inflammatory medications. While these methods can provide relief, they may not fully resolve the condition, particularly in severe cases where adhesions within the joint capsule are substantial.
Surgery – Frozen Shoulder Manipulation Under Anesthesia and Capsular Release
For individuals with persistent symptoms, surgical interventions may be considered. Manipulation under anesthesia involves forcefully breaking the adhesions to restore mobility, while capsular release entails surgically cutting through the thickened capsule. While these procedures can be effective, they come with inherent risks, including postoperative pain, prolonged rehabilitation, and the potential for complications such as nerve injury or infection.2
Innovative Frozen Shoulder Embolization - A Less Invasive Alternative
Principles of Embolization
Embolization is a minimally invasive procedure widely used in various medical fields. In the context of frozen shoulder, embolization involves the injection of agents into blood vessels supplying the joint capsule. This reduces blood flow to the inflamed area, alleviating pain and promoting tissue healing.
Embolization Benefits Over Surgery
Several potential benefits make frozen shoulder embolization an attractive alternative to surgery. Firstly, it is a non-surgical treatment, reducing the risks associated with open surgery. Secondly, the recovery time is one day, and the procedure is performed on an outpatient basis. Patients after embolization go home with just a Band-Aid as opposed to sutures with surgery. Additionally, the risk of postoperative complications, such as infections or nerve injuries, is minimized.3
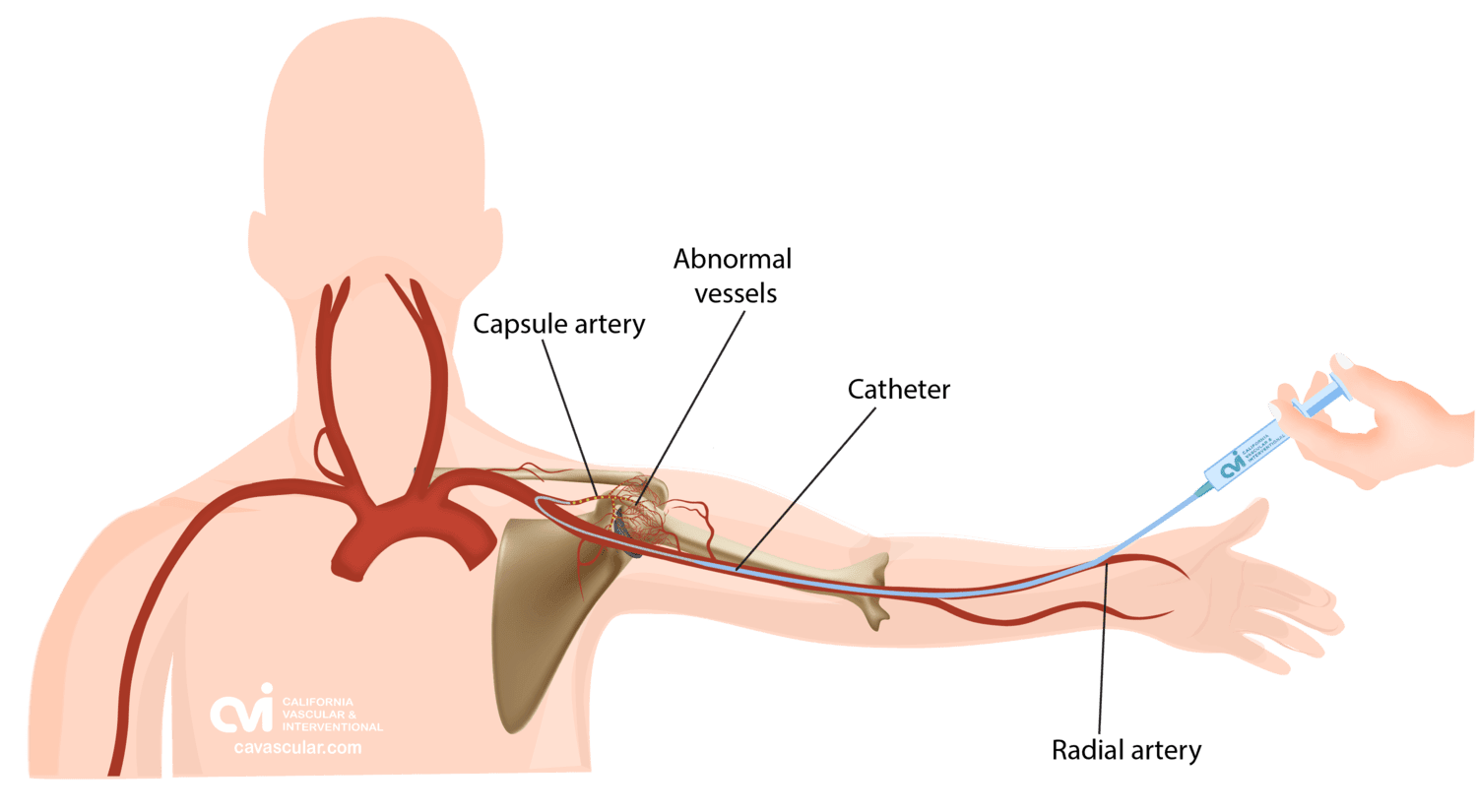
Comparing Risks: Frozen Shoulder Embolization vs. Surgery
Postoperative Pain and Recovery Time
One of the primary advantages of frozen shoulder embolization is the reduced postoperative pain and recovery compared to surgical interventions. There are no surgical incisions with embolization as it is performed through a pinhole in the skin. Surgery often involves cutting or manipulating tissues, leading to more significant discomfort during the recovery period. Embolization, being less invasive, results in less post-procedural pain and a fast recovery.4
Complications
Surgical procedures, particularly capsular release, carry inherent risks of complications such as infection, nerve injury, and bleeding. Embolization, being a catheter-based intervention, minimizes the risk of infection and nerve damage as there is no cutting and there are no major incisions that could introduce an infection. Complications associated with embolization are generally rare but can include bruising or hematoma at the injection site.
Rehabilitation
Postoperative rehabilitation is a crucial aspect of frozen shoulder management. Surgery often necessitates an extended period of physical therapy to regain range of motion. In contrast, embolization might require a shorter rehabilitation period due to the less traumatic nature of the procedure.
Frozen Shoulder Embolization vs Surgery: Satisfaction and Success
Improvement in Pain and Function
Studies suggest that both embolization and surgery can lead to significant improvements in pain and function for individuals with frozen shoulder. However, embolization, with its less invasive nature, may offer comparable outcomes with potentially higher patient satisfaction due to a smoother recovery process.
Quality of Life Considerations
A crucial aspect often overlooked is the impact of the treatment on the patient’s overall quality of life. Embolization, by virtue of being less traumatic and associated with fewer complications, may contribute positively to the patient’s psychological well-being during the recovery phase.5
Frozen Shoulder: Best Treatment
While both frozen shoulder embolization and surgery aim to alleviate pain and improve shoulder function, the choice between the two should be individualized. Embolization offers a less invasive alternative with potential advantages in terms of reduced postoperative pain, quicker recovery, and fewer complications. Those looking to avoid surgical cutting and potential nerve issues can consider embolization as a safer alternative to surgery. Contact our embolization doctor for a thorough discussions to weigh the benefits and risks of each intervention, considering the specific characteristics of the frozen shoulder and the patient’s overall health.
Contact Us Today
Request an appointment to meet with our embolization specialist who will review your imaging and medical records to determine if you are a good candidate and outcomes you can expect. Consultations can be via an online video telehealth platform or in person at one of the offices in Los Angeles, Orange County or San Diego, depending on the doctor’s availability. Why should you choose us? Read here.
References:
- Neviaser RJ, Neviaser TJ, Neviaser JS. Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011;19(9):536-542.
- Buchbinder R, Green S, Youd JM, Johnston RV, Cumpston M. Arthrographic joint distension with saline and steroid improves function and reduces pain in patients with painful stiff shoulder: results of a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;63(3):302-309.
- Soares DP, Riva FM, De Campos JR. Arterial embolization of the shoulder for the treatment of adhesive capsulitis: a pilot study. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2016;27(8):1242-1247.
- Lorbach O, Anagnostakos K, Scherf C, Seil R, Kohn D, Pape D. Nonoperative management of adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: oral cortisone application versus intra-articular cortisone injections. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(2):172-179.
- Omari A, Bunker T. Open surgical release for frozen shoulder: surgical findings and results of the release. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2001;10(4):353-357.
